Last week I started updating EPiServer platform to version 8. The nuget packages were installed without problems, but the update-EPiDatabase powershell command failed because of SQL execution timeout. I was able to run all SQL script via SQL Management Studio. And I did it, but on my local machine only. Of course, I had to upgrade EPiServer database on other developers computers, test, staging and production servers. I was thinking about how to inject custom command with increased timeout.
Running one of the scripts (EPiServer 8.6.0.sql) took about 2,5 minutes. The time was that long because tblActivity table contains more than 3 mln rows. It’s not possible to increase CommandTimeout directly through ConnectionString. This property have to be assigned on the Command object.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 |
Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.8.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.10.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.11.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.12.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.13.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.14.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.16.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.19.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\7.19.1.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\8.0.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\8.4.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.CMS.Core.8.8.1\tools\epiupdates\sql\8.6.0.sql epideploy.exe : At C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.Framework.8.8.1\tools\upgrade.psm1:306 char:3 + &$epiDeployPath -a $action -s $sitePath -p $updatePath\* -c $settings["conne ... + ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ + CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:String) [], RemoteException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : NativeCommandError EPiDeploy was stopped due to an exception, more details: System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException (0x80131904): Timeout expired. The timeout period elapsed prior to completion of the operation or the server is not responding. ---> System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception (0x80004005): The wait operation timed out at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection.OnError(SqlException exception, Boolean breakConnection, Action`1 wrapCloseInAction) at System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.ThrowExceptionAndWarning(TdsParserStateObject stateObj, Boolean callerHasConnectionLock, Boolean asyncClose) at System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.TryRun(RunBehavior runBehavior, SqlCommand cmdHandler, SqlDataReader dataStream, BulkCopySimpleResultSet bulkCopyHandler, TdsParserStateObject stateObj, Boolean& dataReady) at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.RunExecuteNonQueryTds(String methodName, Boolean async, Int32 timeout, Boolean asyncWrite) at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.InternalExecuteNonQuery(TaskCompletionSource`1 completion, String methodName, Boolean sendToPipe, Int32 timeout, Boolean asyncWrite) at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery() at EPiDeploy.Sql.ScriptRunner.<>c__DisplayClass5.<ExecuteScript>b__3() at EPiDeploy.Sql.DatabaseHandler.Execute[T](Func`1 f, Boolean commit) at EPiDeploy.Sql.ScriptRunner.ExecuteScript(StreamReader stream) at EPiDeploy.Sql.ScriptRunner.ExecuteScripts(IEnumerable`1 files, Boolean requiresValidation) at EPiDeploy.Sql.ScriptRunner.<>c__DisplayClass1.<Execute>b__0() at EPiDeploy.Sql.DatabaseHandler.Execute[T](Func`1 f, Boolean commit) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Common.Executor.Execute(ILocation location) at EPiDeploy.Deploy.Execute(Options options, ILocation startPosition) at EPiDeploy.Deploy.Run(Options options) at EPiDeploy.Program.Main(String[] args) ClientConnectionId:97b2e77e-a227-4186-ae98-7bd944e37bd1 Error Number:-2,State:0,Class:11 Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.Commerce.Core.8.13.1\tools\epiupdates_CMS\sql\7.6.0.1.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.Commerce.Core.8.13.1\tools\epiupdates_CMS\sql\8.0.1.0.sql Processing C:\Project\Trunk\lib\EPiServer.Commerce.Core.8.13.1\tools\epiupdates_CMS\sql\8.0.1.2.sql |
EPiDeploy architecture
I looked into EpiDeploy tool code and found out that fortunately it use DbProviderFactory class for creating instance of database connection. DbProviderFactory reads providerName from connectionstring, map this information to assembly type and then instantinate the database connection. Usually System.Data.SqlClient is used as a provider.
|
1 2 |
<add name="EPiServerDB" connectionString="Data Source=(local);Initial Catalog=Project_Dev;Integrated Security=False;User ID=dev;Password=p@55v0rd;MultipleActiveResultSets=True;Connect Timeout=10" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> |
With given SqlConnection provider the epiupdate tool is able to create SqlCommand object. By default SqlCommand timeout is 30 seconds which is not enough. My idea was to replace the factory via providername.
Custom connection factory
The custom provider will be defined in new class library. It will contains just two classes:
- ConfigurableSqlClientFactory – custom connection factory
- ConfigurableSqlConnection – custom connection
The new provider class should inherit from DbProviderFactory class and implement all necessary methods. We cannot simply derive from SqlClientFactory because this class is sealed.
Most of the methods will reuse implementations from System.Data.SqlClient namespace. The only two exceptions are CreateConnection and CreateCommand methods.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
public class ConfigurableSqlClientFactory : DbProviderFactory { // ... public override DbCommand CreateCommand() { var sqlCommand = new SqlCommand {CommandTimeout = 500}; return sqlCommand; } public override DbConnection CreateConnection() { return new ConfigurableSqlConnection(); } // ... } |
We also need to create ConfigurableSqlConnection class that will work similar to SqlConnection class. The CreateDbCommand method is protected in SqlConnection class, so it will be executed by reflection.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
public class ConfigurableSqlConnection : DbConnection { private readonly SqlConnection _connection; public ConfigurableSqlConnection() { this._connection = (SqlConnection)DbProviderFactories.GetFactory("System.Data.SqlClient").CreateConnection(); } protected override DbCommand CreateDbCommand() { var dynMethod = this._connection.GetType() .GetMethod("CreateDbCommand", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance); var dbCommand = (SqlCommand)dynMethod.Invoke(this._connection, new object[] { }); dbCommand.CommandTimeout = 500; return dbCommand; } } |
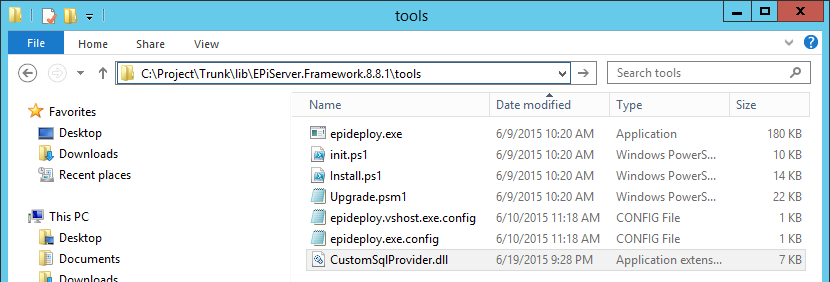
Project output DLL should be placed in epideploy tool directory. Then the application will load library on demand.
Configuring factory
Now the custom factory should be used in EPiServer ConnectionString. The providerName will be set to “ConfigurableConnection”. This name has to be correctly mapped to a .NET type in the application.
Mapping is stored in application configuration file under DbProviderFactories section. So the next step is to create epideploy.exe.config manually and configure provider mapping.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <startup> <supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.5" /> </startup> <system.data> <DbProviderFactories > <add name="CustomSqlProvider" invariant="CustomSqlProvider" description=".Net Framework Data Provider for CUSTOM" type="CustomSqlProvider.ConfigurableSqlClientFactory, CustomSqlProvider, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null" /> </DbProviderFactories> </system.data> </configuration> |
In the end the directory should contain application configuration file and custom provider library.
Full implementation of custom provider classes are available on Gist.